سؤال وجواب

Amplitude mod1
للتحميل اضغط هنا
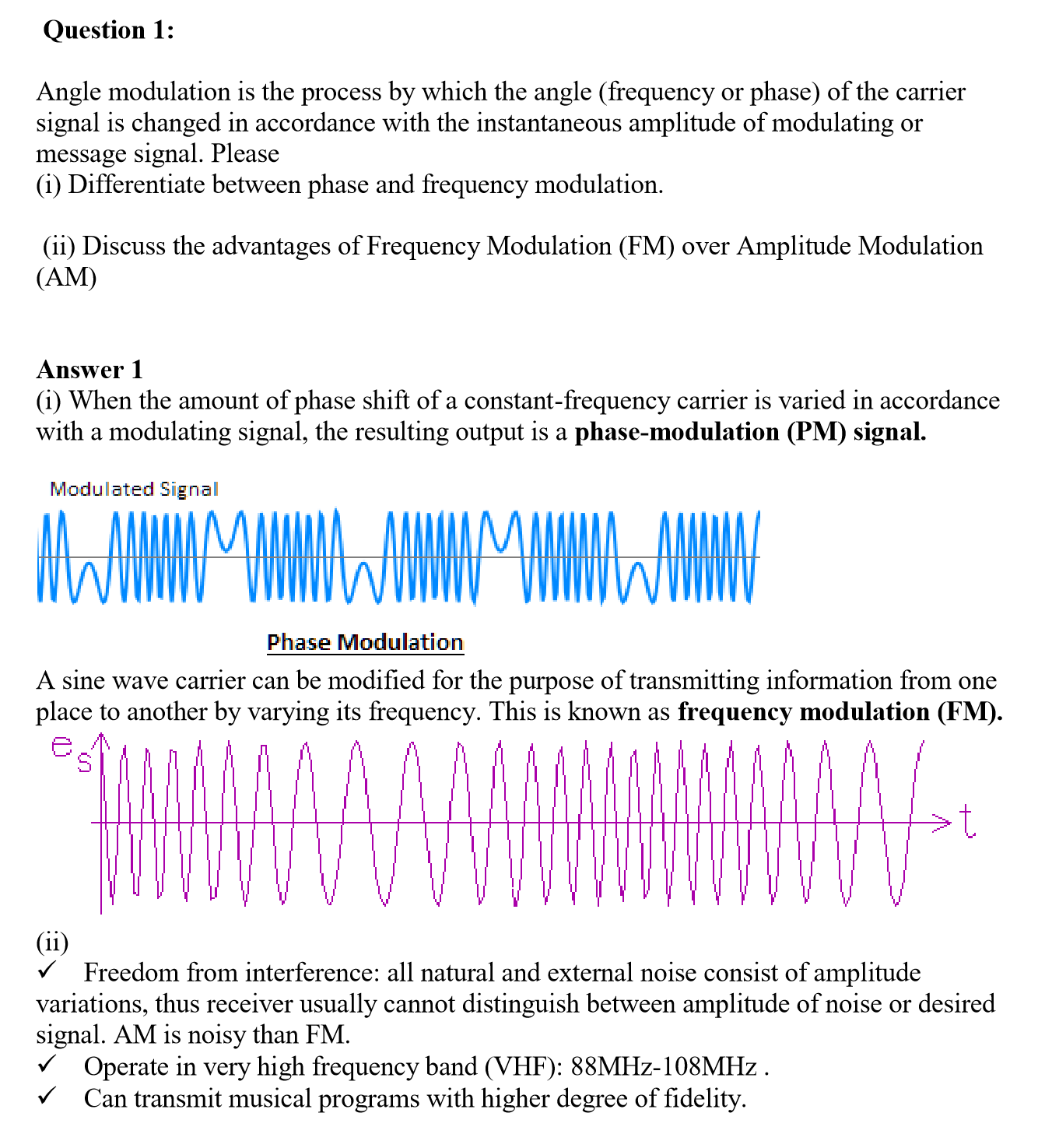

 FILTERING
FILTERING
للتحميل اضغط هنا
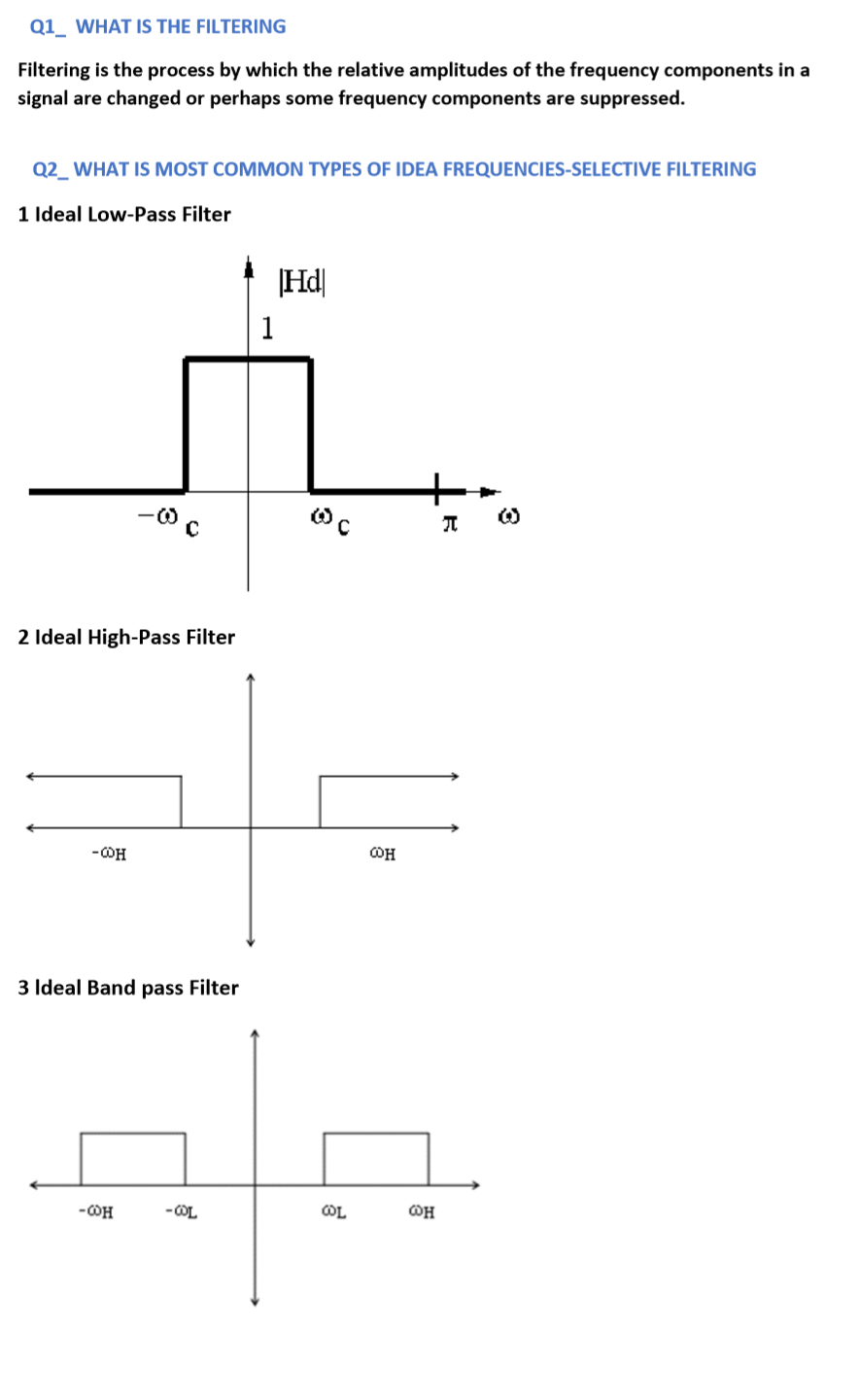
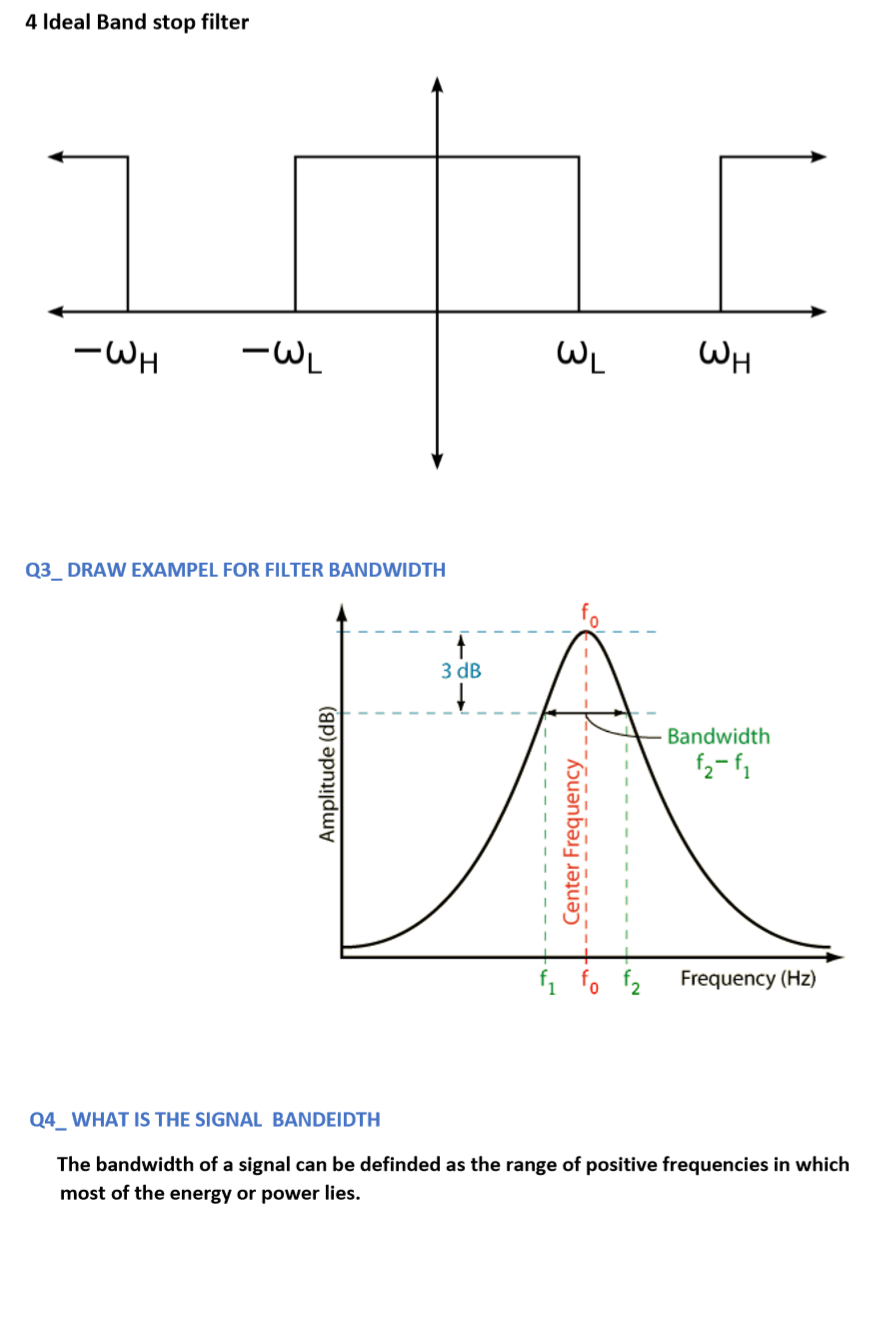 filters and discretes
filters and discretes
للتحميل إضغط هنا
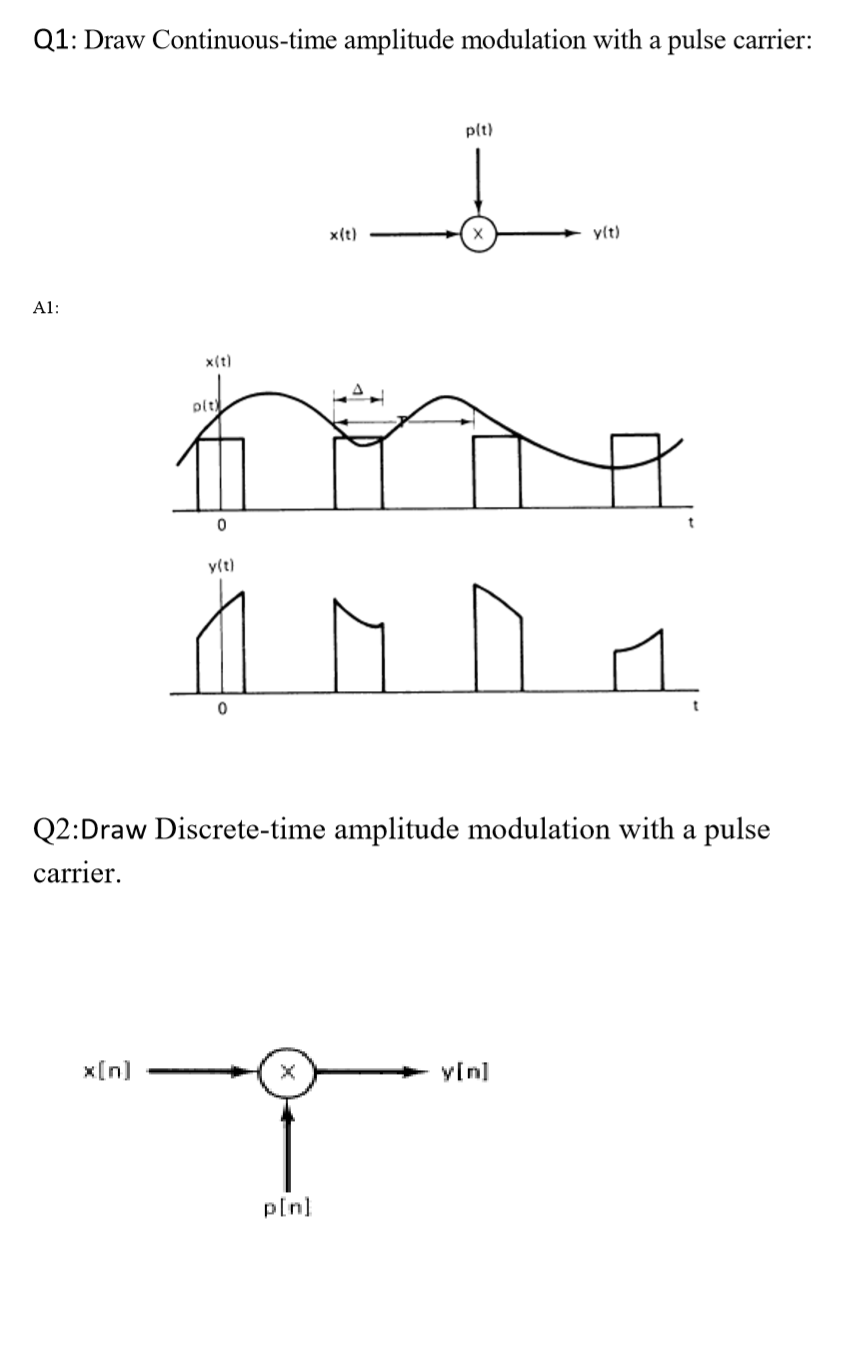
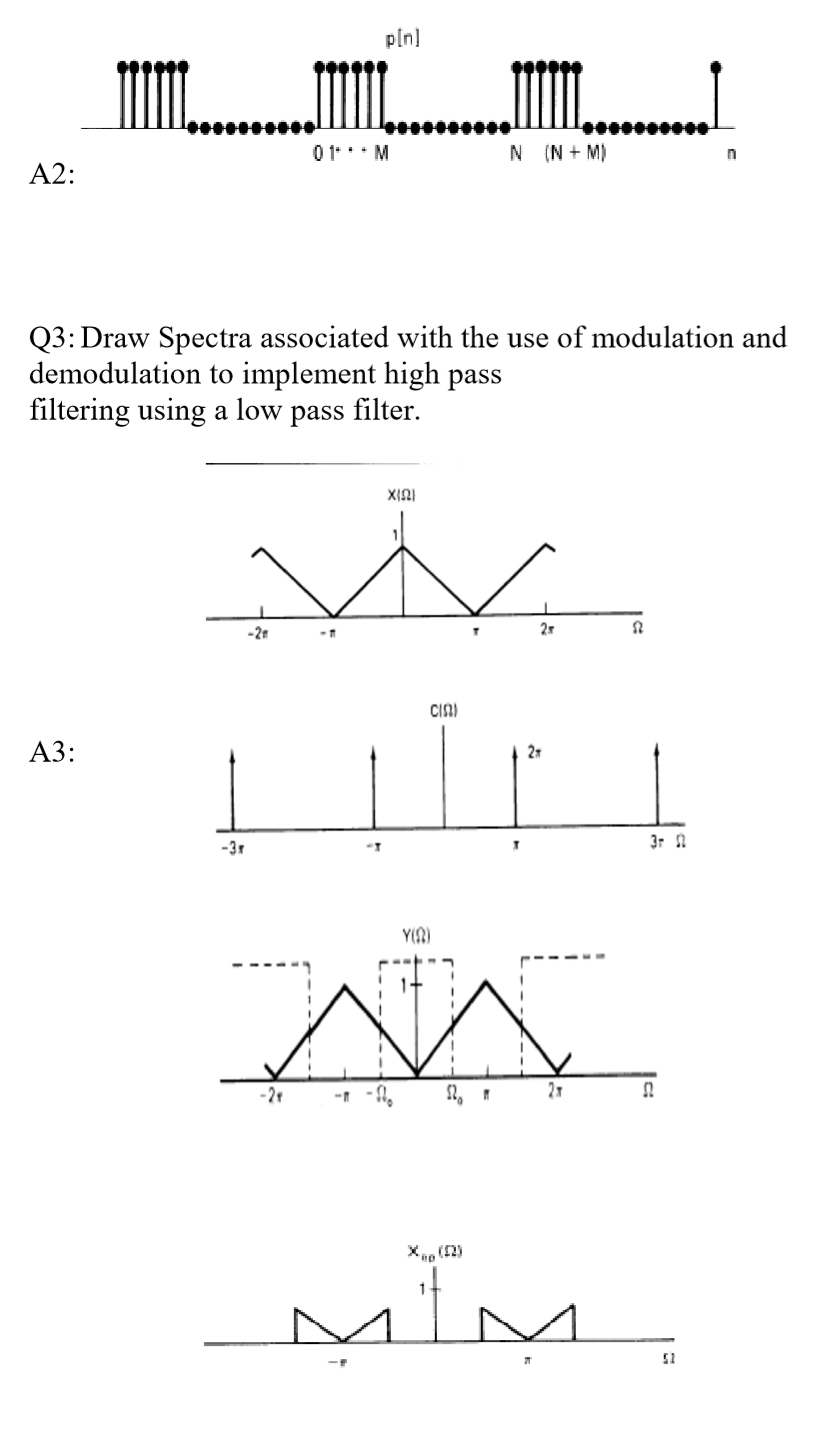
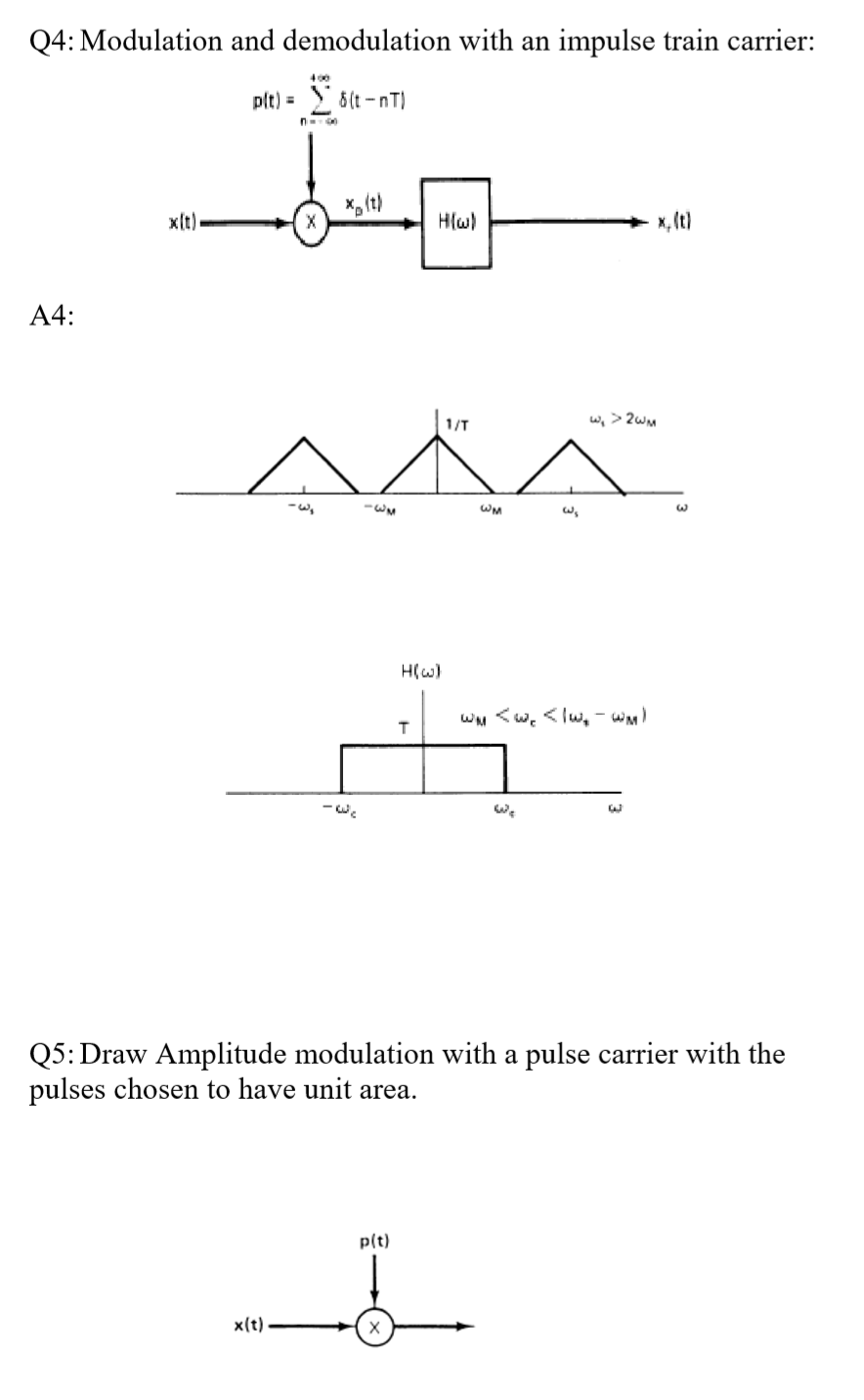
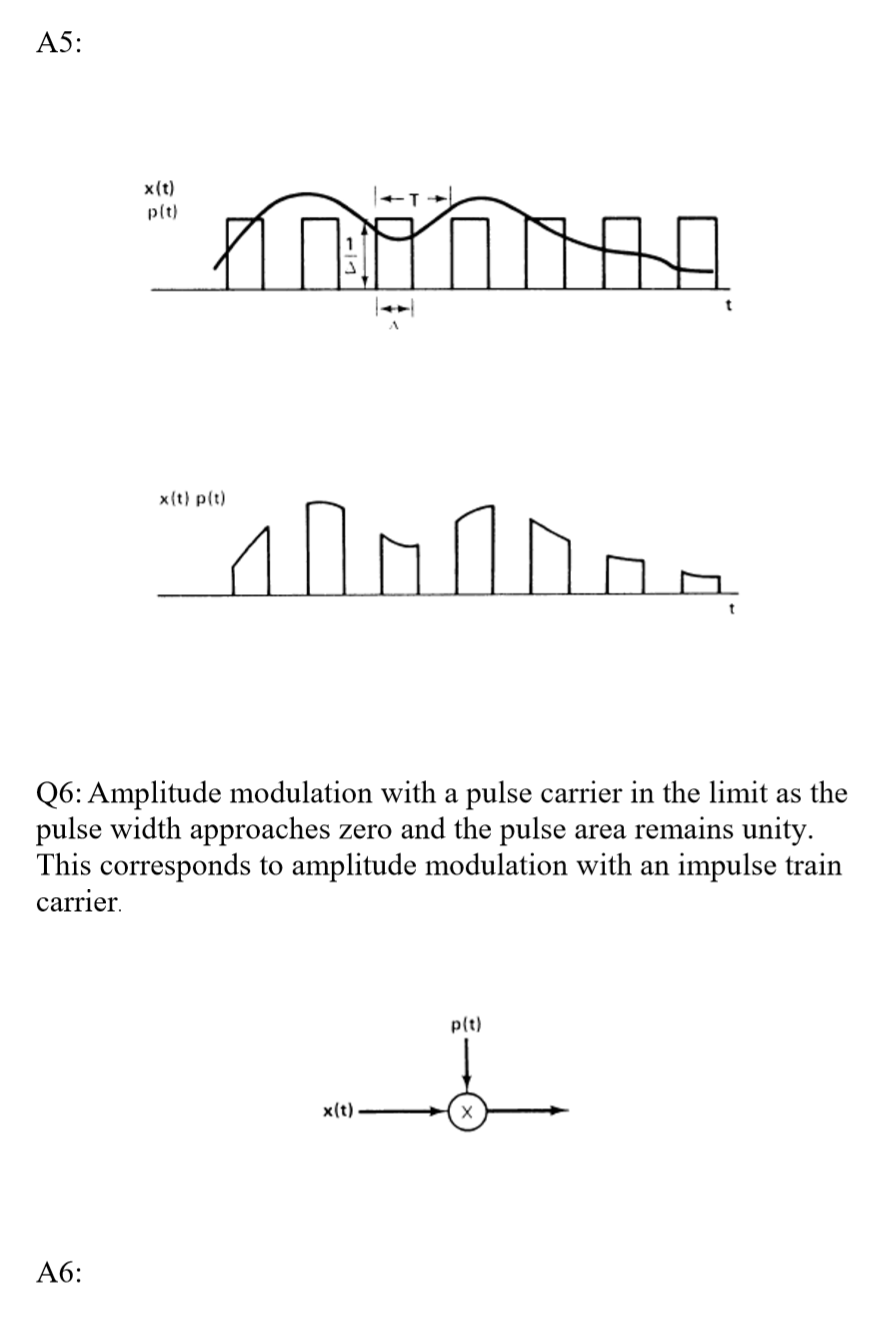
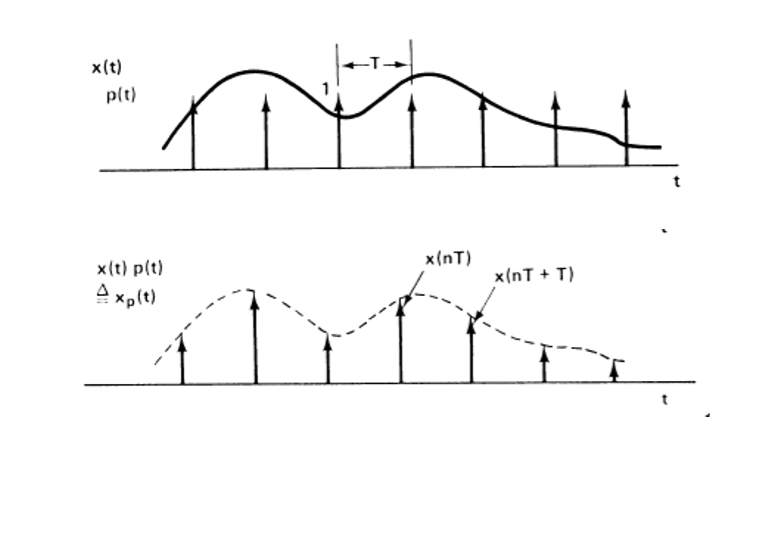
modulation quistions
للتحميل إضغط هنا
1. Define modulation?
Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier
Signal is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating signal.
2. What are the types of analog modulation?
(i) Amplitude modulation.
(ii)Angle Modulation
1. Frequency modulation 2. Phase modulation.
3. Define the term modulation index for AM.
Modulation index is the ratio of amplitude of modulating signal (Em) to amplitude
of carrier (Ec) i.e.m = mEC
4. What are the degrees of modulation?
a) Under modulation (m < 1) b) Critical modulation (m=1)
c) Over modulation(m>1)
5. What is the need formodulation?
Needs for modulation:
a)
b) c)
d) e) f)
Ease of transmission
Multiplexing
Reduced noise
Narrow bandwidth
Frequency assignment
Reduce the equipments limitations.
6. Give the Classification of Modulation.
There are two types of modulation. They are a)Analog modulation
b)Digital modulation
Analog modulation is classified as follows
(i)Continuous wave modulation
(ii)Pulse modulation
Continuous wave modulation is classified as follows
(i)Amplitude modulation
(ii)Double side band suppressed carrier
(iii)Single side band suppressed carrier
(iv)Vestigial side band suppressed carrier
Angle modulation
(i)Frequency modulation
ii)Phase modulation
Pulse modulation is classified as follows
(i)Pulse amplitude modulation (ii)Pulse position modulation
(iii)Pulse duration modulation
(iv)Pulse code modulation
Digital modulation is classified as follows
(i) Amplitude shift keying
(ii)Phase shift keying (iii) Frequency shift keying
7. What is the difference between high level and low level modulation?
In high level modulation, the modulator amplifier operates at high power levels and
delivers power directly to the antenna. In low level modulation, the modulator amplifier
performs modulation at relatively low power levels. The modulated signal is then amplified to high power level by class B power amplifier. The amplifier feeds power to antenna.
8. Define Detection.
Detection is the process of extracting modulating signal from the modulated
carrier. Different types of detectors are used for different types of modulations.
9. Define Amplitude Modulation.
In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of a carrier signal is varied according
to variations in amplitude of modulating signal.
The AM signal can be represented mathematically as, eAM = (Ec + Em sinmt ) sinct
and the modulation index is given as,m = Em EC
10. What is Super Heterodyne Receiver?
The super heterodyne receiver converts all incoming RF frequencies to a fixed lower
frequency, called intermediate frequency (IF). This IF is then amplitude and detected to get the original signal.
11. What is single tone and multi tone modulation?
If modulation is performed for a message signal with more than one
frequency component then the modulation is called multi tone modulation.
If modulation is performed for a message signal with one frequency component then
the modulation is called single tone modulation.
12. Compare AM with DSB-SC and SSB-SC.
S.No AM signal DSB-SC SSB-SC
1 Bandwidth = 2fm Bandwidth = 2fm Bandwidth = fm
2 Contains USB,LSB,Carrier Contains USB,LSB USB,LSB
3 More Power is required for Power required is less than Power required is less than
transmission that of AM.
AM &DSB-SC
13. What are the advantages of VSB-AM?
1. It has bandwidth greater than SSB but less than DSB system.
2. Power transmission greater than DSB but less than SSB system.
3. No low frequency component lost. Hence it avoids phase distortion.
14. How will you generating DSBSC-AM?
There are two ways of generating DSBSC-AM such as a).Balanced modulator
b).Ring modulators
15. What are advantages of ring modulator?
a).Its output is stable.
b). It requires no external power source to activate the diodes.
c).Virtually no maintenance.
d). Long life.
16 .Define Demodulation.
Demodulation or detection is the process by which modulating voltage is recovered
from the modulated signal. It is the reverse process of modulation. The devices used for demodulation or detection are called demodulators or detectors. For amplitude modulation,
detectors or demodulators are categorized as,
a) Square-law detectors
b) Envelope detectors
17. Define Multiplexing.
Multiplexing is defined as the process of transmitting several message
signals Simultaneously over a single channel.
18. Define Frequency Division Multiplexing.
Frequency division multiplexing is definedas many signals are
transmitted simultaneously with each signal occupying a different frequency slot within
a common bandwidth.
19. Define Guard Band.
Guard Bands are introduced in the spectrum of FDM in order to avoid any
interference between the adjacent channels. Wider the guard bands, Smaller the interference.
20. Define SSB-SC.
(i) SSB-SC stands for Single Side Band Suppressed Carrier
(ii) When only one sideband is transmitted, the modulation is referred to as Single
side band modulation. It is also called as SSB or SSB-SC.
21. Define DSB-SC.
After modulation, the process of transmitting the sidebands (USB, LSB) alone
and suppressing the carrier is called as Double Side Band-Suppressed Carrier.
22. What are the disadvantages of DSB-FC?
(i) Power wastage takes place in DSB-FC
(ii) DSB-FC is bandwidth inefficient system.
23. Define Coherent Detection.
During Demodulation carrier is exactly coherent or synchronized in both the
frequency and phase, with the original carrier wave used to generate the DSB-SC wave.
This method of detection is called as coherent detection or synchronous detection.
24. What is Vestigial Side Band Modulation?
Vestigial Sideband Modulation is defined as a modulation in which one of the sideband
is partially suppressed and the vestige of the other sideband is transmitted to compensate for that suppression.
25. What are the advantages of signal sideband transmission?
a) Power consumption
b) Bandwidth conservation c) Noise reduction
26. What are the disadvantages of single side band transmission?
a) Complex receivers: Single side band systems require
more complex and expensive receivers thn conventiaonal AM transmission.
b) Tuning difficulties: Single side band reeivers
require more complex and precise tunig than conventional AM receivers
.
27. Compare linear and non-linear modulators?
S.No Linear Modulators Non Linear Modulators 1. Heavy filtering is not required. Heavy filtering is required.
2. These modulators are used in high These modulators are used in low level
level modulation. modulation.
The carrier voltage is very much The modulating signal voltage is very much
3. greater than modulating signal greater than the carrier signal voltage.
voltage.
28. What is frequency translation?
Suppose that a signal is band limited to the frequency range extending from a
frequency f1 to a frequency f2. The process of frequency translation is one in which the original signal is replaced with a new signal whose spectral range extends from f1' and f2' and which new signal bears, in recoverable form the same information as was borne by the original signal.
29. What are the two situations identified in frequency translations?
a) Up Conversion: In this case the translated carrier frequency is greater
than the incoming carrier
b) Down Conversion: In this case the translated carrier frequency is smaller
than the increasing carrier frequency.
Thus, a narrowband FM signal requires essentially the same transmission bandwidth
as the AM signal.
30. What is BW for AM wave?
The difference between these two extreme frequencies is equal to the bandwidth of
the AM wave.
Therefore, Bandwidth, B = (c + m) - (c - m) B = 2m
31. What is the BW of DSB-SC signal?
Bandwidth, B = (c + m) - (c - m) B = 2
It is obvious that the bandwidth of DSB-SC modulation is same as that of general AM
waves.
32.What are the demodulation methods for DSB-SC signals?
The DSB-SC signal may be demodulated by following two methods: (i) Synchronous detection method.
(ii) Using envelope detector after carrier reinsertion.
33.Write the applications of Hilbert transform?
(i) For generation of SSB signals,
(ii) For designing of minimum phase type filters, (iii) For representation of band pass
signals.
34. What are the methods for generating SSB-SC signal?
SSB-SC signals may be generated by two methods as under:
(i)Frequency discrimination method or filter method. (ii)Phase discrimination method
or phase-shift method.



